Listening includes a lot more than just hearing words. Frequently, we need to interpret or infer a deeper or underlying message beyond the spoken word. We deploy many of our senses to detect non-verbal cues and assimilate our life experiences with the verbal message when we actively listen.
Usually, the objective of a conversation is to expand the listener’s knowledge, perspective or sensitivity to a topic that impacts behavior or beliefs. In the workplace, managing projects can implode due to poor communications. These can result in missing a critical deadline, budget overages, decreased sales, and in some cases, costly lawsuits.
The most effective communication takes place when both parties are actively listening. So what is “active listening” and how do we do this?
Your active listening is apparent to the other party through your audible or visible signals. This can include something as subtle as raising our eyebrows, leaning towards the speaker, or using certain gestures (like a thumbs up, high five, etc.) Tilting our heads when we listen, on the same angle as the speaker, generally reflects a subconscious agreement Uttering sounds like “uh huh” or “hmm” also tell the speaker that you’re paying attention. In America, making eye contact is considered a must in showing that you are listening, although this does vary in some cultures.
Of course asking good questions is one of the best ways to demonstrate that you are listening.
If you don’t have any questions (perhaps, because the message is crystal clear to you) then paraphrase the speaker’s message. You can preface your restated summary by saying something like: “Ok, now, if I understand what you’re telling me, you’d like to … (paraphrased summary of speaker’s objective).”
It is important to be authentic, too! In your effort to make it evident that you genuinely hear the speaker’s message, do not diminish your own persona or credibility. Be sure to phrase your introduction to your rephrased statement in a style that is consistent with the way you speak.
Why not find out if you’re as good a listener as you think you are? If you haven’t taken this insightful (and free) listening assessment yet, you can right now – or later when you have about 45 minutes and no distractions. When you’re ready, take the Active Listening Assessment here. Upon completion, you will receive an explanatory report along with tips and techniques that you can use to become a better active listener and communicator.
If you or your staff would benefit from mastering effective communications, improving active listening and learning “meaning-centered communication”, we can help. Please contact Jim Wynne at jwynne@meritcd.com or call him at 610-225-0449.
NOTE: PMPs®: This assessment qualifies for one PDU® and you will receive a certificate.
PMP and PDU are registered trademarks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
The Pre-Mortem Technique
During my research on how to make better decisions I came across the pre-mortem in the writings of Nobel Prize winner Daniel Kahneman. He notes in his book, Thinking, Fast and Slow (2011), that the pre-mortem technique is valuable in the decision-making process because it has two main advantages.

First, it overcomes “groupthink” that affects many teams once a decision appears to be made. When groupthink is in effect, the wisdom of a plan or decision is gradually suppressed and eventually come to be treated as evidence of disloyalty. The collective suppression of doubt contributes to the group’s overconfidence, which is often a tragic flaw.
Second, it unleashes the imagination of knowledgeable individuals in a much needed direction—the opposite direction of the decision. The principal advantage of the pre-mortem technique is that it legitimizes doubts and encourages everyone, even supporters of the decision, to search for possible threats not considered in the decision-making process. I immediately recognized it as an excellent technique for decision-making, risk management and general leadership.
Because this has proven to be of great value, I would like to share this excellent technique with you. The pre-mortem is easy to implement once the team reaches a decision or finalizes a course of action. Here’s what you need to do:
Step back and state the following: “Imagine that we are one year into the future. We implemented (the decision and plan) exactly as decided here today. The outcome was a total complete disaster. Take 5 to 10 minutes to write a brief history of that disaster.” If someone asks: “What do you mean by a total disaster?” Reply: “In any and every way imaginable it was a total failure.”
Then, explore all the possible reasons that the decision or plan failed. By taking this opposite approach to brainstorming the ideas, your team will likely realize that there are more points that need to be thought through before the plan is implemented.
Merit Career Development incorporates this technique into our leadership, strategic decision-making, risk management and project management classes and it is very well received. In one recent class the participants clutched the flip charts from the group discussion. I saw this and asked what were they going to do with them? I was told that they were going to present the findings to upper management; they had never participated in such a rewarding experience.
Merit can help guide your team through various tools and techniques to optimize your team’s knowledge, skills and ability with techniques and tools such as pre-mortem and many others. Please contact Jim Wynne at jwynne@meritcd.com or call him at 610-225-0449 to schedule training to learn this and other valuable decision-making techniques.

First, it overcomes “groupthink” that affects many teams once a decision appears to be made. When groupthink is in effect, the wisdom of a plan or decision is gradually suppressed and eventually come to be treated as evidence of disloyalty. The collective suppression of doubt contributes to the group’s overconfidence, which is often a tragic flaw.
Second, it unleashes the imagination of knowledgeable individuals in a much needed direction—the opposite direction of the decision. The principal advantage of the pre-mortem technique is that it legitimizes doubts and encourages everyone, even supporters of the decision, to search for possible threats not considered in the decision-making process. I immediately recognized it as an excellent technique for decision-making, risk management and general leadership.
Because this has proven to be of great value, I would like to share this excellent technique with you. The pre-mortem is easy to implement once the team reaches a decision or finalizes a course of action. Here’s what you need to do:
Step back and state the following: “Imagine that we are one year into the future. We implemented (the decision and plan) exactly as decided here today. The outcome was a total complete disaster. Take 5 to 10 minutes to write a brief history of that disaster.” If someone asks: “What do you mean by a total disaster?” Reply: “In any and every way imaginable it was a total failure.”
Then, explore all the possible reasons that the decision or plan failed. By taking this opposite approach to brainstorming the ideas, your team will likely realize that there are more points that need to be thought through before the plan is implemented.
Merit Career Development incorporates this technique into our leadership, strategic decision-making, risk management and project management classes and it is very well received. In one recent class the participants clutched the flip charts from the group discussion. I saw this and asked what were they going to do with them? I was told that they were going to present the findings to upper management; they had never participated in such a rewarding experience.
Merit can help guide your team through various tools and techniques to optimize your team’s knowledge, skills and ability with techniques and tools such as pre-mortem and many others. Please contact Jim Wynne at jwynne@meritcd.com or call him at 610-225-0449 to schedule training to learn this and other valuable decision-making techniques.
Emotional Intelligence (EQ): The Essential Secret to Great Performance
The concept of emotional intelligence, EQ, has been studied for over 30 years. Research shows that high EQ predicts success beyond an individual’s knowledge, skills and abilities. Emotionally intelligent leaders have significantly greater annual profit growth, increased customer satisfaction, and higher personnel retention. In management, the more senior the leader, the more the EQ matters. In sales and customer service capacities, the higher EQs correlate directly to success.
 Studies show that lack of EQ may limit a person’s ability to achieve results. Lower EQ scores correlate with lower merit pay increases, lower job satisfaction and more burnout. Managers’ and supervisors’ EQ scores correlate with their performance ratings.
Studies show that lack of EQ may limit a person’s ability to achieve results. Lower EQ scores correlate with lower merit pay increases, lower job satisfaction and more burnout. Managers’ and supervisors’ EQ scores correlate with their performance ratings.
The definition of emotional intelligence has been the subject of ongoing debates; however, researchers all agree that it consists of two principal components. The first component; intrapersonal skills or self-awareness, is the ability to recognize one’s emotions as they occur, helping one gain self-control in potentially emotionally charged situations.
The second component, interpersonal skills or social awareness, is the ability to recognize others’ emotions. The ability to express empathy enables one to have more positive relationships and minimize unproductive conflict. EQ helps put people at ease, build and mend relationships, confront problem employees, and manage change.
It is important to note that emotional intelligence can be learned. Understanding and incorporating specific EQ skills, techniques, and behaviors can help improve both the intrapersonal and interpersonal skill sets. An intra-personal skill, self-monitoring, can help one can limit or minimize emotional hijacking. Let‘s look at this closer…
 We all have specific words or phrases that are steeped in emotion. During the 1960s and 70s, the term “nuclear power” raised a great deal of emotion—both positive and negative. Similarly today we have emotionally charged words or phrases such as “gun control”, terrorism, and consumer privacy. It is important to recognize one’s own emotionally charged phrases and stop the emotional hijacking that is about to take place.
We all have specific words or phrases that are steeped in emotion. During the 1960s and 70s, the term “nuclear power” raised a great deal of emotion—both positive and negative. Similarly today we have emotionally charged words or phrases such as “gun control”, terrorism, and consumer privacy. It is important to recognize one’s own emotionally charged phrases and stop the emotional hijacking that is about to take place.
By recognizing our emotional responses when we hear a cue by self-monitoring, we can prevent emotional hijacking before it takes place. Stopping to recognize the emotional trigger is an important first step. Taking a deep breath, and/or silently counting to 10 can help us regain composure and react in a rational manner.
As for interpersonal skills, empathy helps us develop more positive relationships with others at work. Increasing our display of empathy enables us to connect with another person on an emotional level, thus allowing us to develop a meaningful, trusting relationship.
The question remains, however, how much emotional intelligence do you have—what is your baseline? Do you have an EQ deficiency, or are you well above average? There is only one way to know your EQ baseline and that is to take an assessment. Many exist on the Internet, some free others fee-based, however they may not stand up to statistical reliability and validity standards.
Would you like some guidance to improve your staff’s EQ? Merit offers half-day and full day workshops that help participants understand, identify their baseline, and strengthen their emotional intelligence. With exercises and interactive assessment tools, this workshop is engaging and life changing. For more information, please contact Jim Wynne at jwynne@meritcd.com or call him at 610-225-0449.
 Studies show that lack of EQ may limit a person’s ability to achieve results. Lower EQ scores correlate with lower merit pay increases, lower job satisfaction and more burnout. Managers’ and supervisors’ EQ scores correlate with their performance ratings.
Studies show that lack of EQ may limit a person’s ability to achieve results. Lower EQ scores correlate with lower merit pay increases, lower job satisfaction and more burnout. Managers’ and supervisors’ EQ scores correlate with their performance ratings.The definition of emotional intelligence has been the subject of ongoing debates; however, researchers all agree that it consists of two principal components. The first component; intrapersonal skills or self-awareness, is the ability to recognize one’s emotions as they occur, helping one gain self-control in potentially emotionally charged situations.
The second component, interpersonal skills or social awareness, is the ability to recognize others’ emotions. The ability to express empathy enables one to have more positive relationships and minimize unproductive conflict. EQ helps put people at ease, build and mend relationships, confront problem employees, and manage change.
It is important to note that emotional intelligence can be learned. Understanding and incorporating specific EQ skills, techniques, and behaviors can help improve both the intrapersonal and interpersonal skill sets. An intra-personal skill, self-monitoring, can help one can limit or minimize emotional hijacking. Let‘s look at this closer…
 We all have specific words or phrases that are steeped in emotion. During the 1960s and 70s, the term “nuclear power” raised a great deal of emotion—both positive and negative. Similarly today we have emotionally charged words or phrases such as “gun control”, terrorism, and consumer privacy. It is important to recognize one’s own emotionally charged phrases and stop the emotional hijacking that is about to take place.
We all have specific words or phrases that are steeped in emotion. During the 1960s and 70s, the term “nuclear power” raised a great deal of emotion—both positive and negative. Similarly today we have emotionally charged words or phrases such as “gun control”, terrorism, and consumer privacy. It is important to recognize one’s own emotionally charged phrases and stop the emotional hijacking that is about to take place.By recognizing our emotional responses when we hear a cue by self-monitoring, we can prevent emotional hijacking before it takes place. Stopping to recognize the emotional trigger is an important first step. Taking a deep breath, and/or silently counting to 10 can help us regain composure and react in a rational manner.
As for interpersonal skills, empathy helps us develop more positive relationships with others at work. Increasing our display of empathy enables us to connect with another person on an emotional level, thus allowing us to develop a meaningful, trusting relationship.
The question remains, however, how much emotional intelligence do you have—what is your baseline? Do you have an EQ deficiency, or are you well above average? There is only one way to know your EQ baseline and that is to take an assessment. Many exist on the Internet, some free others fee-based, however they may not stand up to statistical reliability and validity standards.
Would you like some guidance to improve your staff’s EQ? Merit offers half-day and full day workshops that help participants understand, identify their baseline, and strengthen their emotional intelligence. With exercises and interactive assessment tools, this workshop is engaging and life changing. For more information, please contact Jim Wynne at jwynne@meritcd.com or call him at 610-225-0449.
What Your Peers are Planning
The Results are In!
On behalf of all of us at Merit Career Development, we’d like to thank everyone who participated in our 2nd annual 3-Question Training Planning Survey last month. As promised, we are reporting on the results – which have, interestingly, shifted even from a year ago.Hot Topics

Although project management professionals represented more than 60% of our invitation mailing, the topics in greatest demand for 2016 are Leadership, Team-Building, Communications, and Critical Thinking and Decision-Making. These ranged from 38% to 29%, while the overall category of Project Management (PM) dropped to 13% this year (from 45% last year.) In the PM arena, both years, “Identifying and Managing Project Risks” were in the top third ranking at 29%. See the Q1 chart above for details.
Delivery Methods
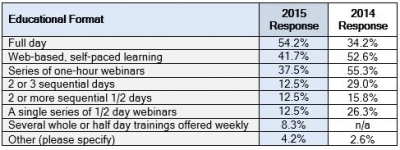
The preferred delivery methods have changed, as well. For the past few years, there was a growing interest in
web-based learning and self-paced, DIY courses. This year, on-site, full day courses have re-gained their
popularity, with 54.4% of respondents choosing this as their preferred delivery method. In 2014 on-site, full day courses were only requested by 34.2% of respondents. For more details, see the Q2 chart.
Choosing the Course and the Provider
 The basis for choosing a course and provider were measured differently last year, but in both instances, the primary driver is the course topic and/or area that most needs development, followed by convenience of timing, and location. The program cost was lower in priority. See Q3 chart on the left for details.
The basis for choosing a course and provider were measured differently last year, but in both instances, the primary driver is the course topic and/or area that most needs development, followed by convenience of timing, and location. The program cost was lower in priority. See Q3 chart on the left for details.If you are seeking to reduce your organization’s gaps in skills, improve cooperation and productivity through better communications and decision-making knowledge, or provide some morale-improving, team-building workshops, let’s talk. With a wide variety of courses, delivery techniques and a highly skilled training team, we will help you achieve your training goals for 2016 and beyond.
Contact Jim Wynne at 610-225-0449 or at jwynne@meritcd.com.
Crossfit Training: Your Body and Your Mind
The start of a new year brings with it many changes, professionally as well as personally. Many of us choose to start the New Year by making goals and resolutions, whether resolving to stick to a budget, or picking up a new hobby. Mine? I’m in the majority of the population: lose weight. To help me achieve my resolution I’ve started an exercise program called CrossFit training.
What is CrossFit training? The CrossFit training program, as explained by its founder Greg Glassman, is a system of performing functional movements that are constantly varied at high intensity. CrossFit is a strength and conditioning program that optimizes physical competence in each of ten recognized fitness domains: Cardiovascular and Respiratory Endurance, Stamina, Strength, Flexibility, Power, Speed, Coordination, Agility, Balance, and Accuracy.
 The CrossFit program was developed to enhance an individual’s competency at all physical tasks. Athletes are trained to perform at multiple, diverse, and randomized physical challenges. This type of fitness is demanded of military and police personnel, firefighters, and many sports requiring overall physical prowess.
The CrossFit program was developed to enhance an individual’s competency at all physical tasks. Athletes are trained to perform at multiple, diverse, and randomized physical challenges. This type of fitness is demanded of military and police personnel, firefighters, and many sports requiring overall physical prowess.
CrossFit training benefits the body by training your individual muscles over time to work together to provide an overall greater level of personal fitness than can be achieved by only conditioning one set of muscles at a time. This got me thinking: are there other areas in my life where I can use this approach? How can I “crossfit” my skills to become better at my job? How can I crossfit new learning opportunities to become a more valuable employee?
How can CrossFit training the body carry over to crossfit training your mind? If we consider our skills, hobbies, and responsibilities in our careers as muscles, we can make the analogy that those skills are muscles needing exercise. Some muscles are used more than others; some are barely used at all. All too often in our jobs, there is a set way of doing things that is like performing a repetitive workout. However, the brain is a muscle that like all muscles must be exercised to be kept in peak condition.
Modern cognitive psychology has demonstrated that the brain is not a static entity. Rather, the brain is continually and constantly developing and pruning pathways across skillsets, linking new knowledge to existing knowledge, or destroying old pathways which aren’t utilized to make room for new synaptic links. You can take advantage of this process by crossfit training your brain with a new skill or area of knowledge, which is seemingly unrelated to your existing career or job responsibilities.
 How can crossfit training your mind benefit you in your workplace? Cross-functional training has many benefits for organizations as well as employees. At an organizational level, cross training skillsets help safeguard the organization against widening skills gaps. Organizations that cross-train employees across a range of functions put themselves in a good position to prevent sudden shortfalls and manage surges in specific areas when there is a spike in demand. On an individual level, cross training enables employees to explore and assess alternative interests and abilities. It also enables managers to identify and nurture employees who show exceptional talent in a particular function. Cross-training yourself to learn new skills, can increase your employability and enable you to stay relevant.
How can crossfit training your mind benefit you in your workplace? Cross-functional training has many benefits for organizations as well as employees. At an organizational level, cross training skillsets help safeguard the organization against widening skills gaps. Organizations that cross-train employees across a range of functions put themselves in a good position to prevent sudden shortfalls and manage surges in specific areas when there is a spike in demand. On an individual level, cross training enables employees to explore and assess alternative interests and abilities. It also enables managers to identify and nurture employees who show exceptional talent in a particular function. Cross-training yourself to learn new skills, can increase your employability and enable you to stay relevant.
A few examples …learning the components of Strategic Leadership as a Project Manager (PM) can help reduce the probability of failure by sharpening leadership skills that enable the PM to better understand, motivate and build consensus with other members of a project team. Or, learning to identify the role emotions and subconscious biases play in the decision making process can enable an individual to make more effective decisions. Learning Risk Management skills can enable a Human Resources manager to better anticipate potential problems and know how to create effective solutions before a problem arises.
In 2016, give consideration to learning things outside the scope of your role or responsibilities. Even if learning new skills may not seem directly related to your current work position, you will be increasing your value. Soon, you’ll wonder how you ever got along without these new skills.
If you are seeking to reduce your organization’s gaps in skills, improve cooperation and productivity through better communications and decision-making knowledge, or provide some morale-improving, team-building workshops, let’s talk. With a wide variety of courses, delivery techniques and a highly skilled training team, we will help you achieve your training goals for 2016 and beyond.
Contact Jim Wynne at 610-225-0449 or at jwynne@meritcd.com.
What is CrossFit training? The CrossFit training program, as explained by its founder Greg Glassman, is a system of performing functional movements that are constantly varied at high intensity. CrossFit is a strength and conditioning program that optimizes physical competence in each of ten recognized fitness domains: Cardiovascular and Respiratory Endurance, Stamina, Strength, Flexibility, Power, Speed, Coordination, Agility, Balance, and Accuracy.
 The CrossFit program was developed to enhance an individual’s competency at all physical tasks. Athletes are trained to perform at multiple, diverse, and randomized physical challenges. This type of fitness is demanded of military and police personnel, firefighters, and many sports requiring overall physical prowess.
The CrossFit program was developed to enhance an individual’s competency at all physical tasks. Athletes are trained to perform at multiple, diverse, and randomized physical challenges. This type of fitness is demanded of military and police personnel, firefighters, and many sports requiring overall physical prowess.CrossFit training benefits the body by training your individual muscles over time to work together to provide an overall greater level of personal fitness than can be achieved by only conditioning one set of muscles at a time. This got me thinking: are there other areas in my life where I can use this approach? How can I “crossfit” my skills to become better at my job? How can I crossfit new learning opportunities to become a more valuable employee?
How can CrossFit training the body carry over to crossfit training your mind? If we consider our skills, hobbies, and responsibilities in our careers as muscles, we can make the analogy that those skills are muscles needing exercise. Some muscles are used more than others; some are barely used at all. All too often in our jobs, there is a set way of doing things that is like performing a repetitive workout. However, the brain is a muscle that like all muscles must be exercised to be kept in peak condition.
Modern cognitive psychology has demonstrated that the brain is not a static entity. Rather, the brain is continually and constantly developing and pruning pathways across skillsets, linking new knowledge to existing knowledge, or destroying old pathways which aren’t utilized to make room for new synaptic links. You can take advantage of this process by crossfit training your brain with a new skill or area of knowledge, which is seemingly unrelated to your existing career or job responsibilities.
 How can crossfit training your mind benefit you in your workplace? Cross-functional training has many benefits for organizations as well as employees. At an organizational level, cross training skillsets help safeguard the organization against widening skills gaps. Organizations that cross-train employees across a range of functions put themselves in a good position to prevent sudden shortfalls and manage surges in specific areas when there is a spike in demand. On an individual level, cross training enables employees to explore and assess alternative interests and abilities. It also enables managers to identify and nurture employees who show exceptional talent in a particular function. Cross-training yourself to learn new skills, can increase your employability and enable you to stay relevant.
How can crossfit training your mind benefit you in your workplace? Cross-functional training has many benefits for organizations as well as employees. At an organizational level, cross training skillsets help safeguard the organization against widening skills gaps. Organizations that cross-train employees across a range of functions put themselves in a good position to prevent sudden shortfalls and manage surges in specific areas when there is a spike in demand. On an individual level, cross training enables employees to explore and assess alternative interests and abilities. It also enables managers to identify and nurture employees who show exceptional talent in a particular function. Cross-training yourself to learn new skills, can increase your employability and enable you to stay relevant.A few examples …learning the components of Strategic Leadership as a Project Manager (PM) can help reduce the probability of failure by sharpening leadership skills that enable the PM to better understand, motivate and build consensus with other members of a project team. Or, learning to identify the role emotions and subconscious biases play in the decision making process can enable an individual to make more effective decisions. Learning Risk Management skills can enable a Human Resources manager to better anticipate potential problems and know how to create effective solutions before a problem arises.
In 2016, give consideration to learning things outside the scope of your role or responsibilities. Even if learning new skills may not seem directly related to your current work position, you will be increasing your value. Soon, you’ll wonder how you ever got along without these new skills.
If you are seeking to reduce your organization’s gaps in skills, improve cooperation and productivity through better communications and decision-making knowledge, or provide some morale-improving, team-building workshops, let’s talk. With a wide variety of courses, delivery techniques and a highly skilled training team, we will help you achieve your training goals for 2016 and beyond.
Contact Jim Wynne at 610-225-0449 or at jwynne@meritcd.com.